Unlock Global Opportunities with LED Lights: A B2B Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for led lights
In today’s rapidly evolving global marketplace, the demand for energy-efficient lighting solutions is at an all-time high. LED lights have emerged as a pivotal choice for businesses seeking to enhance sustainability while reducing operational costs. This shift is particularly pronounced across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where the adoption of advanced lighting technologies is transforming industries ranging from retail to manufacturing.
Understanding the nuances of the LED lighting market is essential for international B2B buyers. The complexities of sourcing high-quality products that meet regional standards, comply with sustainability mandates, and align with local preferences can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the global landscape of LED lights, equipping buyers with critical insights into market trends, supplier selection, regulatory considerations, and best practices for integration.
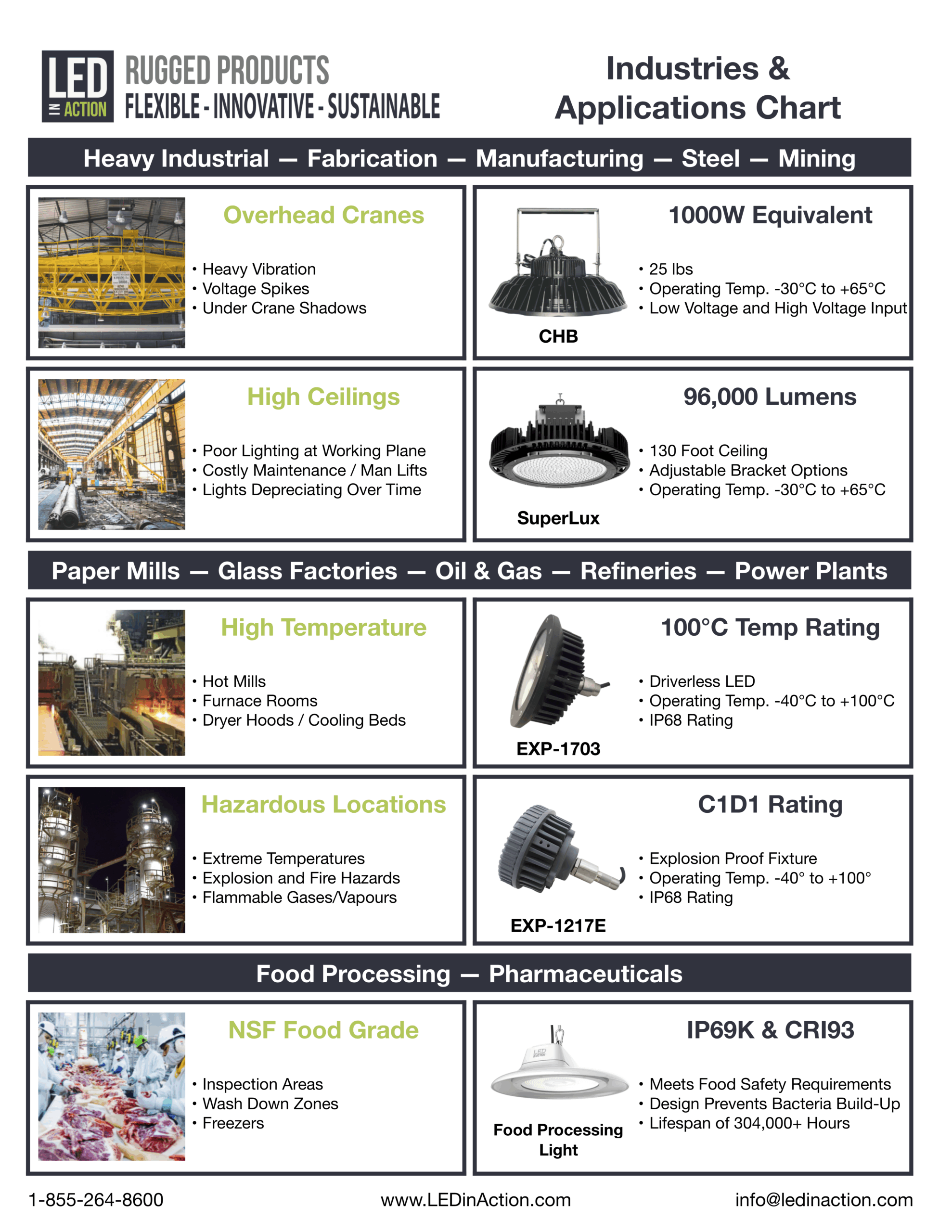
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will explore the advantages of LED technology, delve into the latest innovations, and highlight key players in the market. By leveraging this knowledge, international buyers can make informed decisions that not only optimize their lighting solutions but also contribute to broader environmental goals. Empowering your sourcing strategy with accurate information and actionable insights will be the cornerstone of achieving competitive advantage in this dynamic sector.
Understanding led lights Types and Variations
LED Bulbs
LED bulbs are among the most common types of LED lighting. They provide significant energy savings compared to traditional incandescent and fluorescent lights, boasting a lifespan of up to 25,000 hours. Businesses in retail, hospitality, and office spaces commonly utilize LED bulbs due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. While they are generally reliable, some lower-wattage models may not provide sufficient brightness for larger spaces.
LED Strips
LED strips are flexible light sources that can be cut to size and have adhesive backing for easy installation. They are widely used in signage, interior design, and display applications. Their customizable lengths and colors allow businesses to create unique lighting solutions tailored to their brand or space aesthetic. However, careful installation is necessary to ensure effective lighting coverage and prevent damage to the strips.
High Bay LEDs
High bay LEDs are designed for spaces with high ceilings, such as warehouses, factories, and gyms. They offer high lumen output and wide beam angles, making them ideal for illuminating large areas efficiently. The energy-saving capabilities of high bay LEDs translate into lower operational costs, making them a smart investment for businesses. However, the initial investment may be higher than traditional lighting solutions.
Flood Lights
Flood lights provide broad illumination, making them suitable for outdoor applications like sports facilities and parking lots. They are often weather-resistant, ensuring durability in various environmental conditions. The high visibility they offer is crucial for safety and security in outdoor settings. However, proper positioning is essential to maximize their effectiveness, as poor placement can lead to dark spots.
Smart LEDs
Smart LEDs integrate IoT technology, allowing businesses to control lighting remotely and adjust brightness and color. This adaptability makes them an excellent choice for smart buildings and retail environments where ambiance is key. The energy management capabilities of smart LEDs can lead to significant savings. However, they tend to come at a higher price point and may require more complex installation and setup compared to traditional lighting solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of led lights
Industry Applications
Manufacturing
LED lights are pivotal in manufacturing environments, where they significantly improve factory lighting. Proper illumination enhances visibility, which is essential for workers to perform tasks accurately and safely. By reducing shadows and providing consistent lighting, LED fixtures can help minimize errors and accidents, thus increasing overall productivity. When sourcing, it’s critical to consider energy-efficient models that offer long lifespans, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Retail
In the retail sector, LED lighting is crucial for both display and ambient lighting. The use of LEDs can attract customers and enhance the shopping experience by showcasing products in their best light. This increased visibility can lead to higher sales and customer retention. B2B buyers should focus on color temperature, as different settings can evoke various customer emotions, and consider energy-saving features that contribute to lower operational costs.
Agriculture
LED lighting plays a transformative role in agriculture, especially in greenhouse settings. By providing specific light wavelengths, these lights can optimize growth cycles for various crops, leading to higher yields. This capability allows farmers to extend growing seasons and improve the quality of their produce. Buyers should prioritize sourcing options that are compatible with the specific light spectrum needs of the plants they intend to grow.
Healthcare
In healthcare settings, LED lights are essential for surgical and examination rooms, where accurate lighting is crucial for patient safety and care quality. LEDs provide bright, consistent illumination that reduces eye strain and improves the precision of medical procedures. When sourcing these products, B2B buyers must ensure that the lighting solutions comply with health and safety regulations to maintain a safe environment for both patients and healthcare professionals.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Transportation
LED lighting in transportation, particularly for roadway and tunnel applications, enhances safety by improving visibility for drivers. Well-lit roads and tunnels reduce the likelihood of accidents, contributing to overall public safety. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing options should focus on weather-resistant features and energy efficiency, as these aspects will ensure longevity and reduced maintenance costs in various environmental conditions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for led lights
When selecting materials for LED lights, international B2B buyers must consider several factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in LED lighting, discussing their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and potential applications.
1. Aluminum
Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent thermal conductivity, and is resistant to corrosion. Its thermal properties make it an ideal choice for heat sinks, which are crucial for maintaining LED efficiency and longevity.
Pros:
- Effective Heat Dissipation: Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat, preventing overheating of LED components.
- Lightweight: Makes transportation and installation easier, reducing overall shipping costs.
- Corrosion Resistance: Its natural oxide layer protects against corrosion, ensuring longevity in various environments.
Cons:
- Cost: While generally affordable, high-quality aluminum can be expensive compared to plastic options.
- Durability: Aluminum can be prone to dents and scratches if not treated or coated properly.
Application Impact:
Ideal for commercial and industrial applications where durability and heat management are critical, such as in street lighting and high-bay lighting.
2. Polycarbonate
Properties:
Polycarbonate is a strong, transparent thermoplastic that offers high impact resistance and good optical clarity. It is often used for LED lenses and diffusers.
Pros:
- Impact Resistance: Much stronger than glass, making it suitable for applications where breakage is a concern.
- Lightweight: Reduces transportation costs and simplifies installation.
- UV Resistance: Can be treated to resist yellowing from UV exposure, maintaining clarity over time.
Cons:
- Heat Resistance: While it can withstand moderate temperatures, polycarbonate is less effective at dissipating heat compared to metals.
- Scratching: More prone to scratching than glass, which can affect optical performance.
Application Impact:
Best suited for indoor applications like office lighting or decorative fixtures where safety and aesthetic quality are priorities.
3. Glass
Properties:
Glass is a traditional material known for its clarity, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to scratches. It is often used in high-end lighting designs.
Pros:
- Optical Clarity: Provides excellent light transmission, enhancing the quality of illumination.
- Scratch Resistance: Unlike plastics, glass does not scratch easily, preserving the appearance of light fixtures.
- Thermal Stability: Can withstand high temperatures without deforming.
Cons:
- Weight: Heavier than alternatives like polycarbonate, increasing shipping and installation costs.
- Fragility: More prone to breakage, which can be a safety concern in certain environments.
Application Impact:
Ideal for residential and commercial decorative fixtures where aesthetics and light quality are paramount, such as chandeliers and wall sconces.
4. Steel
Properties:
Steel is a robust material that provides structural strength and durability. It is often used in the housing of LED fixtures.
Pros:
- Strength and Durability: Offers superior structural integrity, ideal for outdoor or industrial applications.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than aluminum while providing similar strength.
Cons:
- Weight: Heavier than aluminum, which can complicate installation and increase shipping costs.
- Corrosion: Requires protective coatings to prevent rusting, especially in humid or coastal environments.
Application Impact:
Commonly used in outdoor lighting, parking lots, and street lighting where strength and weather resistance are critical.
Summary Table
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate material for LED lights hinges on the specific application requirements, including durability, heat management, aesthetic appeal, and cost considerations. B2B buyers should assess these factors carefully to ensure optimal performance and value in their lighting solutions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for led lights
Manufacturing Processes for LED Lights
The manufacturing of LED lights involves a sophisticated process that combines advanced technology and meticulous craftsmanship. Understanding these processes is vital for B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where quality and efficiency are paramount. Below, we outline the typical stages involved in the manufacturing of LED lights, along with key techniques employed.
Main Stages of LED Light Manufacturing
-
Material Selection:
- The first step involves selecting high-quality materials such as semiconductors (typically gallium nitride), phosphors, and substrates (ceramic or metal).
- Buyers should ensure that suppliers source materials from reputable manufacturers to guarantee reliability.
-
Wafer Fabrication:
- This stage involves creating a semiconductor wafer through processes such as epitaxial growth, where a thin layer of semiconductor material is deposited on a substrate.
- Techniques like Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) or Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) are often used to ensure precise control over the material properties.
-
Chip Production:
- After the wafer is fabricated, individual LED chips are cut from the wafer. This is done using a process called dicing.
- Chips are then subjected to photolithography, where light-sensitive materials are used to create patterns that define the LED structure.
-
Die Bonding:
- The LED chips are attached to a heat sink or substrate using die bonding techniques. This ensures effective thermal management, critical for LED longevity.
- Common methods include epoxy bonding and soldering.
-
Wire Bonding:
- Thin wires are connected to the LED chips to facilitate electrical connections. This is typically done using gold or aluminum wire, which is bonded using thermocompression or ultrasonic methods.
-
Encapsulation:
- LEDs are encapsulated with a transparent resin or silicone to protect them from environmental factors while enhancing light output.
- This step often includes the application of phosphor coatings to achieve desired color temperatures and improve color rendering.
-
Assembly:
- The encapsulated LED components are assembled into fixtures or bulbs. This may involve integrating optics, drivers, and heat sinks.
- Automated assembly lines are commonly used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
-
Final Testing:
- Once assembled, the LED lights undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specified performance criteria.
Quality Assurance in LED Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of LED manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Here are the key components and practices associated with quality assurance for LED lights.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to manufacturers aiming to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements consistently.
- IEC 62717: This standard provides specifications for LED modules used in general lighting and helps ensure safety and performance.
- IES LM-79: This standard outlines methods for measuring the electrical and photometric performance of solid-state lighting products.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
- At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival. Buyers should verify that suppliers maintain rigorous IQC processes to ensure only high-quality materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
- During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of components and assembly. This includes checking for defects in die bonding, wire bonding, and encapsulation.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC):
- After assembly, the final products undergo extensive testing to assess their performance, safety, and compliance with relevant standards. This includes thermal testing, photometric testing, and electrical performance evaluations.
Common Testing Methods
- Photometric Testing: Measures luminous flux, efficacy, and color temperature to ensure the LED performs as specified.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses the thermal performance of the LED lights to prevent overheating, which can significantly reduce lifespan.
- Electrical Testing: Verifies that the electrical characteristics meet specifications, including current and voltage ratings.
- Environmental Testing: Tests the LEDs under various environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature) to ensure reliability in real-world applications.
Verifying Quality Control Practices
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are actionable steps to ensure that your LED suppliers adhere to high-quality standards:
- Request Documentation: Ask for certificates demonstrating compliance with relevant international standards (e.g., ISO 9001, IEC 62717).
- Conduct Audits: Consider conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facility to assess their quality control processes and capabilities firsthand.
- Review Test Reports: Request detailed test reports from the manufacturer to understand the results of the FQC process, including any failures and corrective actions taken.
- Seek References: Talk to other businesses that have sourced products from the manufacturer to gauge their reliability and product performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for LED lights is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing and the rigorous quality control checkpoints, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality LED products that meet their operational needs and customer expectations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for led lights Sourcing
When sourcing LED lights for B2B purposes, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The total cost of acquiring LED lighting solutions can be broken down into several key components, each influencing the overall pricing strategy.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary material costs associated with LED lights include the semiconductor chips, circuit boards, lenses, and housing. The quality and type of materials selected can significantly impact the final product cost. For instance, high-quality chips may lead to better energy efficiency and longer lifespan but will also elevate the upfront cost. Buyers should consider sourcing materials that balance quality and price, potentially opting for local suppliers to reduce costs associated with import duties and tariffs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, manufacturers may employ automated processes to offset these expenses. Conversely, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs can lead to significant savings. However, buyers should assess the implications of labor quality on production standards and product reliability.
-
Overhead: This includes fixed and variable costs associated with running a business, such as utilities, rent, administrative salaries, and equipment depreciation. Understanding the manufacturer’s overhead can provide insights into their pricing strategy. Manufacturers with high overhead costs may need to charge more to maintain profitability, influencing the final price offered to buyers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount in the LED lighting industry, where performance and safety standards are critical. The costs associated with quality control processes, including testing and certification, can affect pricing. Buyers should seek suppliers who have robust QC protocols, as this investment often translates into better product performance and reduced failure rates.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting LED lights from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location can vary based on distance, shipping method, and freight rates. For international buyers, understanding the logistics costs is essential. Sourcing from nearby manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, while global sourcing may require careful management of import regulations and logistics fees.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of LED lights beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume: Bulk purchasing often leads to discounts. Buyers should evaluate their needs and consider ordering larger quantities to negotiate better pricing. Manufacturers are typically more willing to offer favorable terms for larger orders, allowing buyers to maximize their budget.
-
Specifications: Customization requests, such as specific color temperatures, wattages, or designs, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements and seek manufacturers who can provide competitive pricing for custom solutions.
-
Quality: Higher-quality products tend to be priced at a premium. However, investing in quality can yield long-term savings through reduced energy consumption and lower replacement rates. Buyers should weigh the upfront costs against the potential Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Leverage the competitive landscape of LED lighting suppliers by negotiating terms. Prepare to discuss pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also lead to better deals in the future.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): TCO encompasses not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and energy costs over the product’s lifespan. Buyers should analyze these factors to make informed decisions that align with their long-term financial goals.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers allows buyers to compare pricing and services. This practice not only fosters competition but also provides insights into market pricing trends, helping buyers make better-informed decisions.
-
Evaluate Supplier Reputation: Consider the supplier’s track record regarding quality, reliability, and customer service. A lower price may not be worth it if the supplier cannot deliver on time or provide the necessary support.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and strategic tips, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing LED lights more effectively, ensuring they achieve both quality and value in their purchases.
Spotlight on Potential led lights Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘led lights’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for led lights
When considering LED lights for commercial applications, B2B buyers must understand both the essential technical properties and the terminology used within the industry. This knowledge is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, ensuring compliance with local regulations, and optimizing operational efficiency.
Key Technical Properties of LED Lights
-
Luminous Efficacy (lm/W)
Luminous efficacy measures how well a light source converts electrical energy into visible light. It is expressed in lumens per watt (lm/W). Higher efficacy indicates a more energy-efficient product, which is vital for reducing long-term operational costs. For instance, an LED light with a luminous efficacy of 100 lm/W is more efficient than one with 70 lm/W, leading to lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint. -
Color Temperature (K)
This property defines the appearance of the light emitted by the LED, measured in Kelvin (K). Lower values (2700K-3000K) produce warm white light, suitable for residential and hospitality applications, while higher values (4000K-6500K) produce cool white or daylight-like light, which is often preferred in commercial and industrial settings. Understanding color temperature helps buyers select products that align with their aesthetic and functional needs. -
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
The CRI measures a light source’s ability to accurately reproduce colors compared to natural light. It is a scale from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating better color accuracy. A CRI of 80 or above is generally acceptable for commercial spaces, while applications requiring precise color matching (e.g., galleries, retail) may benefit from LEDs with a CRI of 90 or higher. -
Lifespan (Hours)
The lifespan of an LED light is a critical factor for B2B buyers, as it affects maintenance costs and operational downtime. Typical LED lights last between 25,000 to 50,000 hours, significantly outlasting traditional incandescent or fluorescent options. Understanding the expected lifespan helps in calculating total cost of ownership and return on investment. -
Dimmability
Not all LED lights are dimmable, and this feature can impact energy savings and the ambiance of a space. Dimmable LEDs allow users to adjust brightness levels, which can lead to additional energy savings and improved comfort. When sourcing LED lights, confirming dimmability and compatibility with existing dimming systems is essential.
Common Trade Terminology in the LED Industry
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEMs produce components or products that are then sold under another company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable manufacturers and secure high-quality products that meet specific requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for international buyers who need to consider inventory costs and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help in planning purchases and negotiating better terms with suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, especially for bulk orders. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, ensuring that the buyer gets the best deal. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. For international buyers, understanding lead times is vital for project planning and inventory management. Factors influencing lead time include production schedules, shipping methods, and customs clearance. -
Certification Standards
Various certification standards (such as CE, RoHS, and UL) indicate that a product meets specific safety and performance requirements. B2B buyers should prioritize products with the necessary certifications to ensure compliance with local regulations and industry standards.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and industry terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies for LED lights, ensuring they select the right products for their needs while optimizing costs and compliance.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the led lights Sector
The LED lights market is experiencing significant growth, driven by various factors such as increasing energy efficiency awareness, regulatory support, and advancements in technology. The global shift towards sustainable energy solutions has propelled LED lighting into the spotlight, with projections estimating the market to reach USD 150 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of over 12%.
In regions like Africa and South America, where energy access remains a challenge, LED lights present a cost-effective solution. Their low energy consumption not only reduces electricity bills but also contributes to energy conservation, making them an attractive option for both residential and commercial sectors. In Europe and the Middle East, stringent regulations aimed at reducing carbon footprints are pushing businesses to adopt LED technology, further accelerating the market’s expansion.
Emerging trends include smart lighting solutions and the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, allowing for enhanced control and energy management. B2B buyers should pay attention to suppliers who are innovating in these areas, as they are likely to offer products that align with future market needs. Additionally, demand for customized lighting solutions tailored to specific industries, such as agriculture and healthcare, is on the rise, presenting opportunities for strategic sourcing.
To capitalize on these trends, international buyers should focus on suppliers that not only provide high-quality products but also demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability.
Sustainability is no longer just a trend; it’s a fundamental aspect of the LED lights sector. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices in their operations. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient production processes, and transparent supply chains.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where local communities are affected by industrial practices. Buyers should seek partnerships with manufacturers who engage in fair labor practices and support local economies. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, as consumers become more environmentally conscious, companies that prioritize sustainability in their product offerings can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty. For international B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers that share these values can facilitate long-term partnerships and foster innovation in sustainable lighting solutions.
The evolution of LED lighting has transformed the landscape of the lighting industry. Initially developed in the early 1960s, LEDs were primarily used for indicator lights and displays due to their high efficiency and long lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. However, it wasn’t until the early 2000s that LED technology began to gain traction in general lighting applications.
This shift was propelled by advancements in semiconductor technology, which enabled the production of high-brightness LEDs suitable for residential and commercial use. The introduction of energy efficiency regulations and growing environmental concerns further accelerated this transition. Today, LED lighting is recognized not only for its energy-saving capabilities but also for its versatility in design and application, making it a preferred choice across various sectors. As the technology continues to evolve, the future of LED lighting looks promising, with ongoing innovations poised to redefine standards in energy efficiency and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of led lights
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of LED lights?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, certifications, and customer reviews. Request samples to evaluate product quality and ensure they meet international standards. It’s also beneficial to visit their manufacturing facilities if possible, or engage in video calls to assess operations. Check for compliance with local regulations in your region, as this can affect product acceptance and safety. Establishing a relationship through clear communication can also help gauge reliability and responsiveness. -
Are LED lights customizable to my specific needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for LED lights, including wattage, color temperature, and design features. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and requirements to the supplier. Inquire about the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for custom designs, as this can vary significantly between manufacturers. It’s advisable to request prototypes before committing to larger orders to ensure the final product aligns with your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for LED lights?
MOQs for LED lights can range widely based on the supplier and product type. Generally, standard products may have lower MOQs, while customized options could require higher quantities. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify your anticipated order volume and seek flexibility. Some suppliers may be willing to accommodate smaller orders for new customers or provide tiered pricing based on order size, which can be advantageous for scaling your purchases. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reliable suppliers should have established QA processes in place, including testing for lumens output, color consistency, and thermal performance. Request documentation of their QA protocols, such as certifications from recognized standards (e.g., ISO 9001). It’s also prudent to ask about their warranty policies and post-sale support, as this can indicate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Regular audits and compliance checks are additional signs of a reputable supplier. -
How do logistics impact the sourcing of LED lights?
Logistics play a crucial role in sourcing LED lights, affecting lead times, shipping costs, and delivery reliability. Consider the geographical location of your supplier and their shipping capabilities. Engage in discussions about shipping methods, incoterms, and potential customs duties. Establish clear timelines for production and delivery to avoid disruptions. Additionally, inquire about their experience in handling international shipments, especially if you are sourcing from regions with different regulatory requirements. -
What should I consider regarding the sustainability of LED light suppliers?
Sustainability is increasingly important in procurement. When sourcing LED lights, evaluate suppliers’ practices regarding energy efficiency, waste management, and sourcing of raw materials. Look for certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and Energy Star, which indicate a commitment to environmental standards. Additionally, inquire about their product life cycle and recyclability options, as sustainable practices can enhance your brand’s reputation and align with consumer preferences. -
How can I ensure compliance with local regulations when sourcing LED lights?
Compliance with local regulations is critical to avoid legal issues and ensure market acceptance. Research the specific standards applicable in your region, such as safety certifications and energy efficiency requirements. Communicate these regulations to your suppliers and confirm their products meet these standards. Request documentation to verify compliance and consider collaborating with local experts or consultants to navigate complex regulatory landscapes effectively. -
What are the best practices for managing communication with suppliers?
Effective communication with suppliers is vital for successful partnerships. Establish clear expectations regarding timelines, product specifications, and payment terms from the outset. Use structured communication methods, such as regular updates and documented agreements, to minimize misunderstandings. Leverage technology tools like project management software for real-time collaboration and updates. Lastly, maintain a professional relationship and be open to feedback to foster trust and enhance cooperation.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement, financial, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure accuracy, we are not responsible for any errors or omissions. Market conditions and company details are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for led lights
As the global demand for LED lighting continues to rise, B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize strategic sourcing to maximize their purchasing power and enhance operational efficiency. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of establishing strong supplier relationships, conducting thorough market analysis, and understanding regional regulations and sustainability standards.
Strategic sourcing not only reduces costs but also fosters innovation, ensuring access to the latest technologies and designs in LED lighting. By prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality, sustainability, and adaptability, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in a competitive marketplace.
Looking ahead, the LED market is expected to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in smart lighting technologies and an increasing focus on energy efficiency. B2B buyers should remain proactive by continuously evaluating their sourcing strategies and exploring new partnerships that align with their sustainability goals. Engage with suppliers who are not only responsive but also visionary, as these collaborations will be crucial in navigating future trends and challenges. Embrace the opportunity to lead in the adoption of innovative lighting solutions that enhance both business performance and environmental responsibility.